Kidney problems can appear suddenly or develop silently over time, and two common conditions that often confuse patients are pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis. Although both affect the kidneys, they occur in different parts, have different causes, and require different treatment approaches. Understanding the difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis is essential for early diagnosis and preventing long-term kidney damage.
According to a Kidney Specialist in Ahmedabad, Dr Ravi Bhadania, many patients struggle to differentiate these conditions because their symptoms may seem similar initially. This detailed guide explains both conditions clearly, covering their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and key differences.
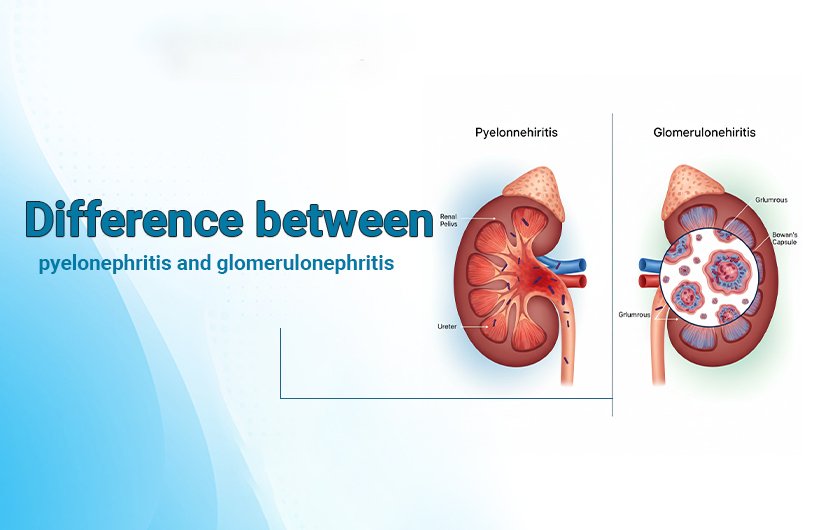
What Is the Difference Between Pyelonephritis and Glomerulonephritis?
Here is a quick overview of how these two conditions differ:
1. Affected Area
- Pyelonephritis: Infection of the renal pelvis and kidney tissue.
- Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the glomeruli, the tiny filters inside the kidneys.
2. Main Cause
- Pyelonephritis: Mostly bacterial infection (usually E. coli).
- Glomerulonephritis: Immune-related inflammation or autoimmune disorders.
3. Symptoms
- Pyelonephritis: Fever, back pain, burning urination, frequent urination.
- Glomerulonephritis: Blood in urine, swelling, high blood pressure, foamy urine.
4. Treatment
- Pyelonephritis: Antibiotics and fluids.
- Glomerulonephritis: Steroids, immunosuppressants, BP control, and dietary changes.
These differences help doctors plan effective treatment and avoid complications.
Pyelonephritis vs Glomerulonephritis
| Feature | Pyelonephritis | Glomerulonephritis |
|---|
| Affected Area | Renal pelvis & kidney tissue | Glomeruli (filtering units) |
| Main Cause | Bacterial infection | Immune-related inflammation |
| Onset | Sudden and severe | Gradual or sudden |
| Key Symptoms | Fever, back pain, burning urination | Blood in urine, swelling, high BP |
| Diagnostic Tests | Urine culture, imaging | Urine protein, blood tests, biopsy |
| Treatment | Antibiotics | Steroids, BP meds, immunosuppressants |
| Complications | Sepsis, kidney abscess | Chronic kidney disease, kidney failure |
What is Pyelonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a bacterial kidney infection, typically starting as a urinary tract infection (UTI) that travels upward to the kidneys. It may affect one or both kidneys and requires immediate treatment.
Causes of Pyelonephritis
The most common cause is E. coli, a bacteria normally present in the gut. Other causes include:
- Kidney stones or urinary blockage
- Enlarged prostate
- Poor hygiene (common in children or elders)
- Vesicoureteral reflux (urine flowing backward)
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Weak immune system
Symptoms of Pyelonephritis
Symptoms usually appear suddenly:
- High fever with chills
- Pain in lower back or sides
- Frequent urination
- Burning sensation during urination
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Nausea or vomiting
- Extreme fatigue
Diagnosis of Pyelonephritis
Doctors may perform:
- Urine test (bacteria, pus, blood)
- Urine culture to identify bacteria
- Ultrasound or CT scan for severe cases
Treatment for Pyelonephritis
Treatment includes:
- Antibiotics (oral or IV)
- Pain relievers
- Increased fluid intake
- Hospitalization for severe infections
Prompt treatment prevents kidney damage or sepsis.
What is Glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the glomeruli, the filtering units that clean blood and remove waste. It can be acute (sudden onset) or chronic (slowly progressive).
Causes of Glomerulonephritis
Unlike pyelonephritis, bacterial infection is not the primary cause. Factors include:
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., lupus)
- Immune system disorders
- Viral infections (Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C)
- Streptococcal throat infection
- IgA nephropathy
- High blood pressure
- Long-term diabetes
- Sometimes idiopathic (unknown cause)
Symptoms of Glomerulonephritis
Symptoms may develop gradually:
- Blood in urine (cola-colored or red)
- Foamy urine due to protein loss
- Swelling in face, legs, and feet
- High blood pressure
- Reduced urine output
- Fatigue and nausea
Diagnosis of Glomerulonephritis
Tests may include:
- Urine test (protein & blood)
- Blood test (creatinine & urea)
- Ultrasound
- Kidney biopsy (most accurate test)
Treatment for Glomerulonephritis
Treatment is based on the cause and severity:
- Steroids to reduce inflammation
- Blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors/ARBs)
- Diuretics for swelling
- Immunosuppressant medicines
- Low-salt, low-protein diet
- Dialysis in severe cases
Diagnosis Difference: Pyelonephritis vs Glomerulonephritis
| Condition | Primary Diagnostics | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Pyelonephritis | Urine culture, imaging | Detect bacterial infection |
| Glomerulonephritis | Urine protein, blood tests, biopsy | Confirm inflammation & kidney damage |
Treatment Difference: Pyelonephritis vs Glomerulonephritis
- Pyelonephritis → Antibiotics + supportive care
- Glomerulonephritis → Immune control, BP management, long-term monitoring
Which Condition Is More Serious?
Both can be serious if untreated:
- Glomerulonephritis poses a higher long-term risk and may lead to chronic kidney disease.
- Pyelonephritis, if untreated, can cause sepsis, a life-threatening infection.
Prompt treatment significantly reduces complications.
When Should You See a Kidney Specialist?
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Back pain with fever
- Blood in urine
- Swelling around eyes or feet
- Foamy urine
- Reduced urine output
- High blood pressure
- Recurrent urinary infections
Dr Ravi Bhadania advises that early diagnosis can prevent permanent kidney damage.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis helps patients recognize symptoms early and seek correct treatment. Pyelonephritis is primarily a bacterial infection, while glomerulonephritis is an immune-related inflammation. Both conditions can be managed effectively with timely treatment and regular monitoring.
If you or a loved one notices warning signs such as fever, blood in urine, swelling, or persistent fatigue, consult a kidney specialist immediately. Early care is the key to protecting long-term kidney health.
FAQs
What is the main difference between pyelonephritis and glomerulonephritis?
Pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection of the kidney, while glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the kidney’s filtering units due to immune reactions.
Which is more dangerous: pyelonephritis or glomerulonephritis?
Glomerulonephritis has more long-term risks, but pyelonephritis can become life-threatening if it leads to sepsis.
Can pyelonephritis turn into glomerulonephritis?
No. They have different causes, bacterial vs immune-related.
How is glomerulonephritis confirmed?
A kidney biopsy is the most definitive diagnostic test.